Written By:
Scott McAuley
Scott is the IT Director of Texas Management Group, and has been in the IT industry for 25 years.
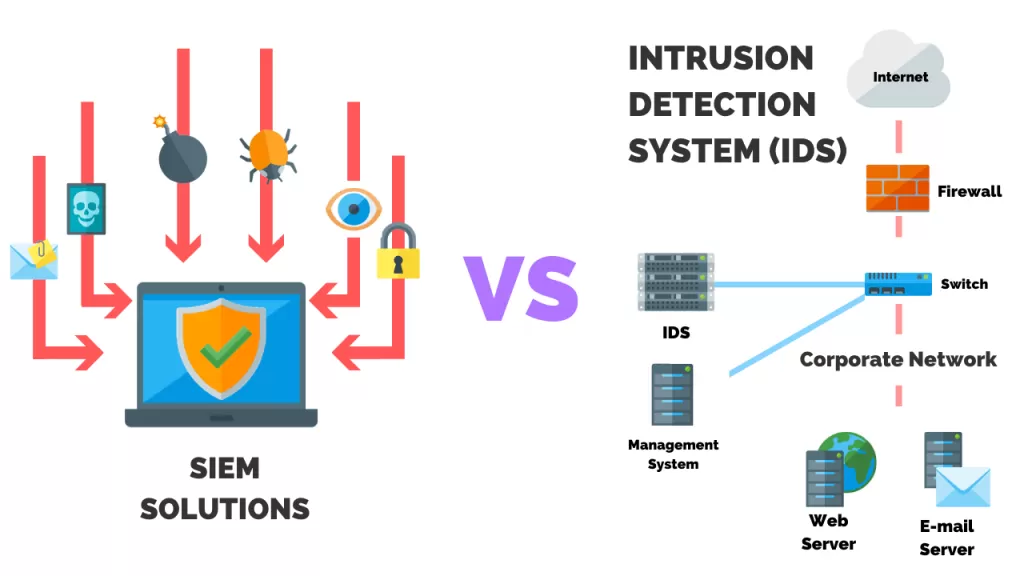
In the high-stakes world of cybersecurity, choosing the right tools can mean the difference between a fortified defense and a vulnerable network.
Two of the most critical technologies are SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) and IDS (Intrusion Detection Systems). But when it comes to SIEM vs. IDS, what sets them apart?
In this article, we’ll uncover the 5 key differences that can enhance your cybersecurity strategy. Ready to dive into the nuances of SIEM and IDS and discover which one is right for your security needs?
Let’s explore how these tools differ and how they can work together to protect your organization.
Key Takeaways
- SIEM offers holistic security by aggregating data from multiple sources, while IDS focuses on detecting specific threats in real-time.
- SIEM’s advanced analytics help identify complex threat patterns, whereas IDS uses signature-based and anomaly detection for immediate alerts.
- SIEM systems excel in compliance reporting and automated incident response, while IDS primarily generates real-time alerts.
- IDS requires manual intervention for response, while SIEM integrates with SOAR tools to automate incident response workflows.
- Combining SIEM and IDS provides layered defense, enhancing both immediate and long-term threat protection for your organization.
Table of Contents
SIEM vs. IDS: Definitions and Features
In the cybersecurity domain, Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) are pivotal for protecting digital assets.
They serve unique roles and operate distinctively. Understanding their definitions is key to grasping their roles in your cybersecurity strategy.
What is Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)?
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) is a comprehensive security solution designed to provide real-time analysis of security alerts generated by applications and network hardware.
SIEM systems aggregate, analyze, and correlate log data from various sources across your network, centralizing log management and security analytics for enhanced threat detection and incident response.
Key Functions of SIEM:
- Log Event Collection and Management: Aggregates log data from multiple sources such as firewalls, servers, and applications.
- Data Analysis: Analyzes log events to identify patterns, detect anomalies, and correlate data for comprehensive threat insights.
- Incident Management and Response: Facilitates the swift identification and response to security incidents, minimizing potential damage.
- Dashboards and Reporting: Provides customizable dashboards and reports for real-time monitoring and historical analysis.
- Threat Detection and Compliance: Supports the detection of potential threats and helps maintain regulatory compliance through continuous monitoring.
5 SIEM Features and Capabilities
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems are critical for maintaining robust cybersecurity. They offer a range of features that help organizations monitor, detect, and respond to security threats effectively.
Here are five key SIEM features and capabilities:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Aggregation | Centralizes data from various sources, offering a comprehensive view of security events. |
| Correlation | Identifies patterns and detects complex threats by analyzing aggregated data, reducing false positives. |
| Dashboards | Provides real-time, visual security insights through customizable interfaces. |
| Alerting | Sends real-time notifications of potential security incidents based on predefined rules. |
| Automation | Automates repetitive tasks like log analysis and incident response, enhancing security efficiency. |
1. Data Aggregation
SIEM systems gather data from various sources like firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and antivirus tools.
2. Correlation
SIEM systems detect complex threats by identifying patterns and anomalies in the aggregated data.
3. Dashboards
SIEM dashboards offer real-time, visual updates on security metrics like detected threats and device statuses.
4. Alerting
SIEM systems trigger real-time alerts for potential security threats based on predefined rules.
5. Automation
SIEM automation streamlines tasks like log analysis and incident response, minimizing manual effort and errors.
What is an Intrusion Detection System (IDS)?

An Intrusion Detection System (IDS) is a cybersecurity tool designed to monitor network and system activities for signs of malicious behavior or policy violations.
IDS works in real-time, analyzing network traffic and system events to detect potential security breaches.
Key Functions of IDS:
- Monitoring: Continuously monitors network traffic and system activities for suspicious behavior.
- Detection: Identifies potential intrusions using two primary detection methods:
- Signature-based Detection: Compares network traffic patterns against a database of known attack signatures to identify malicious activity. This method is highly effective against known threats but may not detect new or unknown attacks.
- Anomaly-based Detection: Uses machine learning algorithms to establish a baseline of normal system behavior and alerts on deviations from this baseline. This method is adept at identifying novel threats but can generate false positives.
5 IDS Features and Capabilities
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) are vital for network security, continuously monitoring for malicious activities. Here are five key features and capabilities of IDS:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Real-time Monitoring and Alerting | Continuous traffic monitoring with immediate alerts for suspicious activities. |
| Advanced Threat Detection | Uses algorithms and machine learning to identify known and emerging threats. |
| Log Management and Analysis | Generates and analyzes detailed logs for forensic and historical review. |
| Compliance Reporting | Provides reports to help meet regulatory and security standards. |
| Incident Response and Remediation | Facilitates quick containment and mitigation of security breaches. |
1. Real-time Monitoring and Alerting
IDS provide continuous surveillance of network traffic, detecting suspicious activities and sending immediate alerts to security teams.
2. Advanced Threat Detection
Leveraging sophisticated algorithms and machine learning, IDS identify a wide range of threats, including zero-day exploits and malware.
3. Log Management and Analysis
IDS generate detailed logs of all monitored activities, crucial for forensic analysis and historical review.
4. Compliance Reporting
IDS assist in meeting regulatory requirements by providing comprehensive reporting capabilities.
5. Incident Response and Remediation
IDS support swift incident response by providing detailed information about detected threats.
SIEM vs. IDS: How They Work and Why They are Important to Cybersecurity
SIEM and IDS are crucial in cybersecurity, focusing on monitoring and detecting threats. They differ in their approaches to analyzing data for potential security incidents.
Grasping their functions is key to a strong cybersecurity strategy, offering real-time alerts and aiding in incident response.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
How Does SIEM Work?
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) works by collecting, analyzing, and correlating log data from various sources within an organization’s IT infrastructure.
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how SIEM operates:
- Data Collection:
- SIEM gathers log and event data from diverse sources, including servers, applications, network devices, and security systems.
- This data is collected in real-time and sent to a centralized SIEM platform.
- Data Aggregation and Normalization:
- The collected data is aggregated and normalized to ensure consistency and to facilitate easier analysis.
- Normalization involves converting different log formats into a standardized format.
- Data Analysis and Correlation:
- SIEM uses predefined rules, machine learning algorithms, and statistical correlations to analyze the log data.
- It categorizes data into various event types, such as successful and failed logins, malware activity, and other suspicious activities.
- Threat Detection:
- SIEM identifies potential security threats by analyzing data patterns and correlating events across multiple sources.
- It uses User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA) to detect abnormal behavior by comparing current activities against a baseline of normal behavior.
- Alert Generation:
- When SIEM identifies potential security issues, it generates alerts based on predefined rules and thresholds.
- Alerts are prioritized based on the severity of the detected threat. For example:
- A user account with multiple failed login attempts over an extended period might generate a low-priority alert.
- A user account with a high number of failed login attempts in a short period might generate a high-priority alert, indicating a possible brute-force attack.
- Incident Response:
- SIEM systems often integrate with Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) tools to automate incident response processes.
- This integration helps security operations centers (SOCs) respond to threats more quickly and efficiently by automating routine tasks.
- Reporting and Compliance:
- SIEM provides detailed reports and dashboards for real-time monitoring and historical analysis.
- These reports help organizations meet regulatory compliance requirements and conduct forensic investigations.
5 Benefits of Using a SIEM
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems are integral to modern cybersecurity strategies, offering comprehensive monitoring and analysis of security data.
Here are five key benefits of using a SIEM:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Real-Time Threat Recognition | Immediate detection and alerts for security threats. |
| AI-Driven Automation | Automates tasks like log analysis using AI. |
| Improved Organizational Efficiency | Centralizes data, enhancing efficiency. |
| Detecting Advanced and Unknown Threats | Uses machine learning to identify sophisticated threats. |
| Conducting Forensic Investigations | Provides detailed logs for investigations. |
1. Real-Time Threat Recognition
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems provide immediate detection and alerting of potential security threats.
2. AI-Driven Automation
SIEM solutions leverage artificial intelligence to automate repetitive security tasks, such as log analysis and correlation.
3. Improved Organizational Efficiency
By centralizing and streamlining security data from various sources, SIEM enhances overall efficiency.
4. Detecting Advanced and Unknown Threats
SIEM systems utilize advanced analytics and machine learning to identify sophisticated and previously unknown threats.
5. Conducting Forensic Investigations
SIEM solutions offer comprehensive logging and reporting features, which are essential for forensic investigations.
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
How Does IDS Work?
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) monitor network traffic to identify potential security breaches or malicious activities. Here’s how IDS operates in detail:
1. Signature-based Detection:
- Mechanism: Compares network traffic against a database of known attack signatures.
- Alert Trigger: If a match is found, an alert is generated.
- Use Case: Effective against known threats.
2. Anomaly-based Detection:
- Mechanism: Establishes a baseline of normal network behavior.
- Alert Trigger: Flags deviations from this baseline as potential threats.
- Use Case: Useful for detecting unknown or new threats.
5 Benefits of Using an IDS
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) play a crucial role in safeguarding an organization’s network infrastructure.
Here are five key benefits of implementing an IDS in your security strategy:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Early Threat Detection | Monitors and alerts for suspicious activities in real time. |
| Improved Incident Response | Enables quicker responses through timely breach alerts. |
| Security Visibility | Provides insight into network traffic and user behavior. |
| Compliance Support | Helps meet regulatory requirements with documented evidence. |
| Reduced Risk of Data Breaches | Monitors for unauthorized access, lowering breach risks. |
1. Early Threat Detection
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) provide real-time monitoring and alerts for suspicious activities, enabling early identification of potential threats.
2. Improved Incident Response
With an IDS in place, security teams receive timely notifications about potential breaches, facilitating quicker and more efficient responses.
3. Security Visibility
IDS offer comprehensive visibility into network traffic and user activities, helping organizations understand normal and abnormal behavior patterns.
4. Compliance Support
Implementing an IDS helps organizations meet regulatory requirements and industry standards by providing documented evidence of security measures.
5. Reduced Risk of Data Breaches
By continuously monitoring for unauthorized access and malicious activities, IDS reduce the likelihood of data breaches.
SIEM vs. IDS: 5 Key Differences
Understanding the differences between SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) and IDS (Intrusion Detection Systems) is crucial for building a robust cybersecurity strategy.
Both tools play vital roles, but they serve different purposes within an organization’s security infrastructure.
| Feature | SIEM | IDS |
|---|---|---|
| Functionality | Holistic security monitoring and incident response | Specific threat detection within network traffic or host systems |
| Scope | Broad coverage across entire IT infrastructure | Narrow focus on network traffic or host systems |
| Alerting and Reporting | Advanced alerting, prioritization, and compliance reporting | Real-time alerts with limited reporting capabilities |
| Response Capabilities | Integration with SOAR for automated incident response | Lacks built-in response capabilities, requires manual intervention |
| Data Analysis | Advanced analytics for identifying complex threat patterns | Signature-based and anomaly-based detection methods |
1. Functionality
SIEM systems provide a comprehensive security overview by aggregating and analyzing log data from various sources, including IDS, firewalls, antivirus tools, and more.
This holistic approach enables security teams to detect, investigate, and respond to threats efficiently.
IDS, on the other hand, focuses on monitoring network or host activities to detect specific malicious actions and policy violations.
It alerts security personnel to potential security breaches, operating in real-time to identify known threats and anomalies.
2. Scope
SIEM systems have a broad scope, managing logs and analytics across the entire IT infrastructure, including networks, servers, applications, and endpoints.
This extensive coverage allows SIEM to offer insights into a wide range of security events.
IDS is more specialized, concentrating on detecting specific types of malicious activities within network traffic or on host systems. Its narrow focus makes it highly effective for immediate threat detection.
3. Alerting and Reporting
SIEM excels in alerting and reporting, with advanced features for threat prioritization based on risk and impact.
It generates customizable reports for compliance purposes and provides a centralized dashboard for monitoring security events.
IDS primarily generates real-time alerts for suspicious activities but offers limited reporting capabilities. It’s designed to quickly notify security teams of potential threats, leaving more in-depth analysis to tools like SIEM.
4. Response Capabilities
SIEM often integrates with SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response) platforms, automating incident response workflows.
This integration allows for rapid incident containment and remediation, enhancing the overall response efficiency.
IDS, as a detection tool, lacks inherent response capabilities. It requires manual intervention or integration with other security tools to respond to detected threats.
5. Data Analysis
SIEM employs advanced analytics, including machine learning and behavioral analysis, to uncover complex threats and anomalies across diverse data sources.
It correlates events from multiple systems to detect sophisticated attacks.
IDS uses signature-based and anomaly-based detection methods to identify known threats and unusual behavior in network or host systems.
While effective for immediate threat detection, it lacks the comprehensive analytical capabilities of SIEM.
Conclusion
In today’s cybersecurity landscape, integrating SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) and IDS (Intrusion Detection Systems) is essential.
SIEM offers centralized monitoring and long-term threat detection, while IDS focuses on real-time anomaly detection. Together, they create a multi-layered defense, providing comprehensive protection against both immediate and evolving threats.
Combining the strengths of both SIEM and IDS ensures robust, proactive defense and better protection for your digital assets.
Take action now to fortify your cybersecurity strategy—integrate these solutions and stay ahead in a constantly changing threat environment. In cybersecurity, being proactive is key to staying secure.
Need Help Deciding Between SIEM and IDS for Your Business?
Check out our blog section for comparisons and insights into essential cybersecurity tools. Discover how our managed cybersecurity services offer robust protection and expert support.
Get in touch today to build a stronger defense!
FAQ
What is the Difference Between SIEM and Cyber Security?
SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) is a tool for monitoring and analyzing security events, while cyber security encompasses all practices and technologies to protect systems and data from cyber threats.
What is the Difference Between Identity and Access Management and SIEM?
Identity and Access Management (IAM) controls user access and authentication, while SIEM aggregates and analyzes security data to detect and respond to threats.
Is a SIEM and IPS?
No, SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) is not the same as an IPS (Intrusion Prevention System). SIEM collects and analyzes security data, while IPS actively prevents and blocks threats.
What is the Difference Between SIEM and Cyber SOAR?
SIEM focuses on collecting and analyzing security data for threat detection, while Cyber SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response) automates and coordinates responses to security incidents.