Written By:
Scott McAuley
Scott is the IT Director of Texas Management Group, and has been in the IT industry for 25 years.
In the ever-changing world of cybersecurity, understanding the tools available is critical.
Among the most powerful are IDS (Intrusion Detection Systems) and IPS (Intrusion Prevention Systems). But what is IDS and IPS, and how do they protect your network?
In this article, we’ll break down these key technologies and explore five important similarities and differences. Mastering IDS and IPS can mean the difference between a secure network and potential threats.
Ready to strengthen your cybersecurity strategy? Let’s explore how IDS and IPS work together to protect your digital assets.
Key Takeaways
- Both IDS and IPS are crucial cybersecurity tools that detect and respond to potential threats, enhancing network security.
- Both systems use signatures and behavior models to identify threats, automate responses, and simplify regulatory compliance across modern enterprises.
- IDS passively monitors and alerts, while IPS actively prevents threats, making them complementary in a robust security strategy.
- IDS sits inside the network for visibility, while IPS is inline, actively filtering and blocking malicious traffic to prevent damage.
- Employing IDS and IPS together provides comprehensive defense, merging real-time threat detection and prevention for optimal network security.
Table of Contents
What is IDS and IPS?
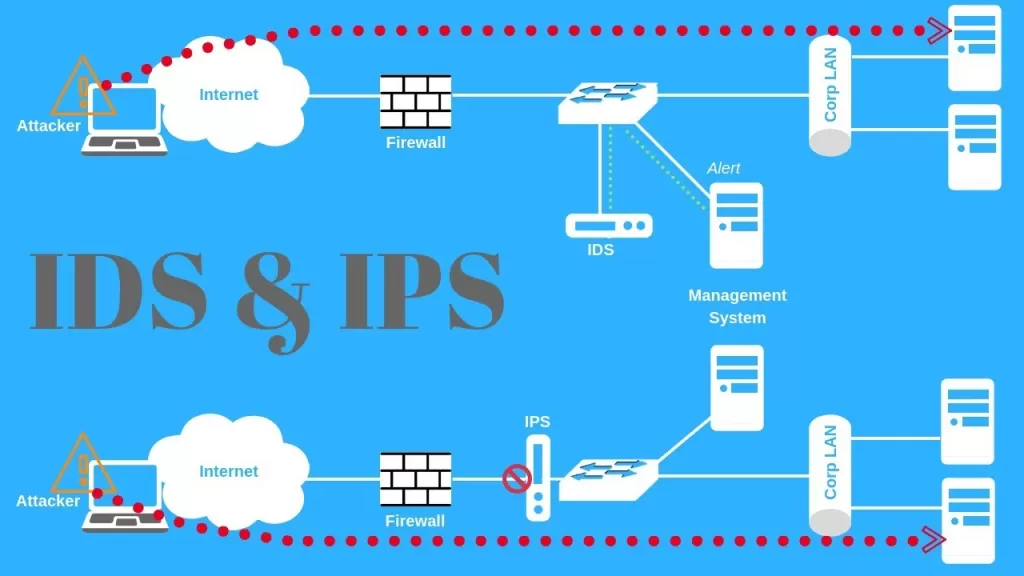
In the realm of cybersecurity, Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) are critical components for protecting network integrity and data security.
Both systems monitor network traffic to identify potential threats, but they operate differently and serve distinct purposes.
Intrusion Detection System (IDS)
An IDS is a passive monitoring system that scrutinizes network traffic for signs of unauthorized or malicious activity.
It uses a database of known threat signatures, which are patterns associated with various types of malware, such as viruses, worms, and ransomware.
When network data packets match these threat signatures, the IDS generates alerts to notify network administrators of potential security breaches.
Since IDS operates out-of-band, it does not interfere with the flow of network traffic but provides comprehensive visibility into potential threats.
Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)
An IPS, on the other hand, is an active security system that not only detects but also responds to threats in real-time. Integrated inline with the network traffic, an IPS analyzes and controls network access to prevent malicious activities.
When the IPS identifies suspicious or malicious packets, it can take immediate action by dropping the packets, terminating connections, or reconfiguring firewalls to block further attacks.
This proactive approach ensures that threats are neutralized before they can cause harm.
How Does an IDS Work?
An Intrusion Detection System (IDS) is a vital component in network security, designed to monitor, detect, and alert administrators to suspicious activities within network traffic.
IDS work by analyzing data packets and comparing them against a set of predefined criteria to identify potential security threats.
Detection Methods:
| Detection Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Signature-Based (SIDS) | Compares network packets against a database of known threat signatures to detect familiar malicious activities. |
| Anomaly-Based (AIDS) | Monitors traffic against a predefined baseline of normal behavior, using machine learning to identify abnormal patterns and potential threats. |
| Reputation-Based | Evaluates the reputation scores of network entities to identify potential threats based on historical behavior and credibility assessments. |
1. Signature-Based Detection:
Signature-based IDS detect attacks by searching for specific patterns or sequences in network traffic that match known malicious signatures. These signatures are predefined and stored in a database.
This method is highly effective at identifying known threats but may struggle to detect new, unknown attacks for which no signature exists.
2. Anomaly-Based Detection:
Anomaly-based IDS monitor network traffic and compare it to a baseline of normal activity. Any deviation from this baseline is flagged as suspicious.
This method employs machine learning to create models of normal behavior, making it capable of detecting previously unknown threats.
However, anomaly-based detection can generate more false positives compared to signature-based detection.
3. Reputation-Based Detection:
Reputation-based IDS assess the credibility of sources by assigning reputation scores to network entities based on their historical behavior.
Potential threats are identified based on these scores, providing an additional layer of threat assessment.
5 Main Types of IDS
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) are vital for protecting your network from cyber threats. The FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center reported over 800,000 complaints in 2021, resulting in losses near $7 billion.
Let’s discuss the five primary IDS types and their distinct capabilities:
| IDS Type | Key Features | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Network IDS (NIDS) | Analyzes all inbound and outbound traffic; real-time monitoring | Detecting network-wide threats |
| Host IDS (HIDS) | Installed on individual devices; monitors traffic, processes, and files | Combating insider threats and endpoint-specific attacks |
| Protocol-Based IDS (PIDS) | Monitors specific protocols like HTTP or HTTPS | Securing web servers and protocol-specific communications |
| Application Protocol-Based IDS (APIDS) | Specializes in application security; installed on server groups | Protecting critical applications and server communications |
| Hybrid IDS | Combines multiple IDS approaches for comprehensive protection | Organizations seeking customized, multi-layered security solutions |
1. Network Intrusion Detection System (NIDS)
A Network Intrusion Detection System (NIDS) analyzes all network traffic in real-time. It operates at a strategic network point, detecting suspicious activities swiftly.
Network Node Intrusion Detection Systems (NNIDS) are a subset of NIDS, offering quicker speeds and using fewer resources.
2. Host Intrusion Detection System (HIDS)
Host Intrusion Detection Systems (HIDS) monitor specific devices within your network. They focus on network traffic, device processes, and file changes.
This allows HIDS to combat insider threats and detect malicious activities at a detailed level.
3. Protocol-Based Intrusion Detection System (PIDS)
Protocol-Based Intrusion Detection Systems (PIDS) concentrate on specific protocols, like HTTP or HTTPS.
They ensure web servers’ security by analyzing protocol traffic. PIDS can spot anomalies and threats targeting these critical channels.
4. Application Protocol-Based Intrusion Detection System (APIDS)
Application Protocol-Based Intrusion Detection Systems (APIDS) focus on securing applications across servers.
They monitor server communication and analyze application protocols. APIDS can identify and block attacks on your critical applications.
5. Hybrid Intrusion Detection System
Hybrid Intrusion Detection Systems combine signature-based and anomaly-based detection. This approach offers a comprehensive security solution.
Hybrid systems provide better threat detection, fewer false positives, and broader coverage against known and unknown threats.
How Does an Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) Work?
An Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) is a proactive network security tool designed to monitor, detect, and prevent malicious activities in real-time.
Unlike an Intrusion Detection System (IDS), which only alerts administrators to potential threats, an IPS actively takes measures to block or mitigate those threats, ensuring that network security is maintained.
Detection Methods:
| Detection Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Signature-Based Detection | Monitors network packets against a database of known attack patterns (signatures). Identifies and blocks packets that match known threats to prevent network compromise. |
| Statistical Anomaly-Based Detection | Establishes a baseline of normal network behavior and detects deviations from this baseline. Effective for identifying new threats but may generate false positives. |
| Stateful Protocol Analysis Detection | Examines network traffic to ensure adherence to predefined protocol standards. Detects deviations that indicate potentially malicious activity. |
1. Signature-Based Detection:
Signature-based IPS monitors network packets and compares them against a database of known attack patterns, known as signatures.
When a packet matches a signature, the IPS identifies it as a potential threat and takes immediate action to block it.
2. Statistical Anomaly-Based Detection:
Anomaly-based IPS establishes a baseline of normal network behavior by analyzing traffic patterns, bandwidth usage, and protocol activities. It then monitors network traffic and identifies deviations from this baseline.
While this method is effective at detecting new threats, it can also generate false positives if legitimate activities exceed the established baseline.
3. Stateful Protocol Analysis Detection:
This method involves examining network traffic to ensure that it adheres to predefined protocol standards.
By comparing observed events with established profiles of normal protocol behavior, stateful protocol analysis can detect deviations that may indicate malicious activity.
4 Main Types of IPS
Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) are categorized into four primary types, each addressing different network security facets. These systems aim to shield against diverse cyber threats, ensuring the network’s safety and integrity.
Here are the 4 main types of IPS:
| IPS Type | Focus Area | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| NIPS | Network traffic analysis | Inspects packets, blocks malicious content |
| WIPS | Wireless network protection | Detects rogue access points, prevents unauthorized access |
| NBA | Unusual traffic flows and patterns | Leverages analytics and machine learning for anomaly detection |
| HIPS | Host-level activity monitoring | Analyzes system calls, logs, and file modifications |
1. Network-Based Intrusion Prevention System (NIPS)
A Network-based Intrusion Prevention System (NIPS) is positioned strategically within the network to scan for suspicious activities. It inspects all network traffic, searching for malicious content or abnormal behavior.
2. Wireless Intrusion Prevention System (WIPS)
Wireless Intrusion Prevention Systems (WIPS) are tailored for wireless network security.
Wireless networks are inherently more susceptible to attacks, making WIPS crucial for detecting and thwarting unauthorized access and other wireless threats.
3. Network Behavior Analysis (NBA)
Network Behavior Analysis (NBA) zeroes in on identifying unusual traffic patterns within the network. By setting a baseline of normal network behavior, NBA can pinpoint anomalies and potential threats.
This IPS utilizes advanced analytics and machine learning to uncover sophisticated attacks, like zero-day exploits and insider threats, which traditional methods might miss.
4. Host-Based Intrusion Prevention System (HIPS)
A Host-based Intrusion Prevention System (HIPS) is installed on individual devices within the network. It scrutinizes the activities and events on the host, examining system calls, application logs, and file modifications.
Top 5 Similarities Between IDS and IPS
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) are key tools in cybersecurity, designed to protect networks from various threats.
While they serve different functions, these systems share several important similarities that make them essential for safeguarding modern enterprises.
Here are the similarities between IDS and IPS:
| Similarity | Description |
|---|---|
| Designed for Modern Enterprises | Both systems integrate with current IT environments to protect against cyber threats. |
| Use Signature Databases or Behavior Models | Detect threats through known attack patterns or unusual network behavior. |
| Utilize Automation | Automate continuous monitoring and instant response to threats. |
| Simplify Compliance | Provide logs to help meet regulatory requirements like GDPR and HIPAA. |
| Help Enforce Security Policies | Control access to network resources and ensure only authorized users can interact with sensitive data. |
1. Help Enforce Security Policies
IDS and IPS are also crucial for enforcing business security policies. They can be set up to monitor and control access to network resources, ensuring that only authorized users can handle sensitive data.
This strengthens the organization’s overall security by preventing unauthorized access and protecting valuable assets.
2. Designed for Modern Enterprises
Both IDS and IPS are built to address the security challenges faced by today’s businesses.
They help protect sensitive information, prevent disruptions, and avoid reputational damage by integrating seamlessly with current IT systems. This ensures companies can stay secure in an increasingly digital world.
3. Use Signature Databases or Behavior Models
Both systems rely on two main methods for threat detection: signature-based and behavior-based.
Signature-based detection matches known attack patterns from a database, while behavior-based detection looks for unusual activity that could signal a new threat.
This combination helps both IDS and IPS identify a variety of attacks, from familiar malware to new, emerging threats.
4. Utilize Automation
Automation is central to both IDS and IPS, allowing them to monitor traffic continuously and respond to threats instantly.
This reduces the need for manual input, letting security teams focus on complex tasks while ensuring faster threat detection and response.
5. Simplify Compliance
Compliance with regulations is a major concern for organizations, and both IDS and IPS help meet these requirements.
They keep logs of network activities and security incidents, which can be used to prove compliance with standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. This makes it easier for companies to avoid penalties and maintain customer confidence.
Top 5 Differences Between IDS and IPS
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) are key cybersecurity tools, but they serve different purposes. Understanding their differences is essential for choosing the right one for your security strategy.
Here are the main differences between IDS and IPS:
| Difference | IDS (Intrusion Detection System) | IPS (Intrusion Prevention System) |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Monitors and alerts but doesn’t take action. | Detects and automatically blocks or mitigates threats. |
| Placement | Inside the network to monitor traffic, but not inline. | Inline with traffic, actively filtering and blocking threats. |
| System Type | Can be network-based (NIDS) or host-based (HIDS). | Primarily network-based, inspecting all network traffic. |
| Anomaly Response | Alerts security teams, requires human intervention. | Automatically blocks or mitigates threats in real-time. |
| Performance | Minimal impact on network performance, no latency. | Can introduce latency due to real-time traffic analysis. |
1. Function
- IDS: A passive system that monitors traffic for suspicious activity and alerts security personnel. It doesn’t stop or block threats.
- IPS: An active system that detects threats and automatically blocks or mitigates them in real-time, preventing attacks from progressing.
2. Placement
- IDS: Typically placed inside the firewall to monitor network traffic, providing visibility but not blocking it.
- IPS: Positioned inline with network traffic, inspecting and filtering all data, and blocking any malicious packets before they enter the network.
3. System Type
- IDS: Can be network-based (NIDS) to monitor overall traffic or host-based (HIDS) to monitor specific devices.
- IPS: Primarily network-based, inspecting all network traffic and responding in real-time to detected threats.
4. Anomaly Response
- IDS: Detects and alerts on suspicious activity but requires human intervention to address the threat.
- IPS: Automatically blocks or mitigates threats without needing human input, providing faster response times.
5. Performance
- IDS: As it passively monitors traffic, it has minimal impact on network performance and doesn’t introduce latency.
- IPS: Since it actively analyzes and blocks traffic in real-time, it can cause latency, so proper configuration is critical for optimal performance.
Which is Better: IDS or IPS?
When deciding between IDS (Intrusion Detection System) and IPS (Intrusion Prevention System) for network protection, it’s essential to understand their distinct roles and benefits.
Both IDS and IPS are valuable for different reasons, and often, a combination of both provides the best security solution.
IDS focuses on monitoring network traffic and alerting administrators of suspicious activity without taking direct action. This passive approach ensures that legitimate traffic is never blocked, but it requires human intervention to address potential threats.
IPS goes a step further by actively blocking malicious traffic in real-time. This proactive stance helps to prevent attacks before they can cause damage but can also lead to false positives, potentially disrupting legitimate network activities.
Choosing Between IDS and IPS:
- IDS is suitable for organizations that prefer to have visibility into network traffic without the risk of blocking legitimate activities. It’s ideal for environments where human intervention is available to respond to alerts.
- IPS is better for organizations that need real-time protection and can tolerate occasional disruptions from false positives. It is particularly useful in environments where immediate threat prevention is critical.
Best Practice:
Many companies find that using both IDS and IPS together provides the most robust protection. By leveraging the monitoring capabilities of IDS and the proactive defenses of IPS, organizations can create a comprehensive security strategy.
Conclusion
Mastering network security involves a clear understanding of IDS (Intrusion Detection Systems) and IPS (Intrusion Prevention Systems).
These technologies share common goals but operate differently, each providing unique benefits. IDS passively monitors and alerts, while IPS actively blocks threats.
Both use advanced detection methods to identify and mitigate potential cyber threats, offering comprehensive security when used together.
Ready to strengthen your defenses? Explore IDS and IPS solutions today and safeguard your network from cyber threats. Have questions or insights? Join the conversation and share your experiences.
Curious About Implementing IDS and IPS for Better Security?
Browse our blogs to learn about the key differences and benefits. See how our IT software solutions provide comprehensive security tools to keep your network safe.
Contact us today for expert support!
FAQ
What are the Differences Between IDS and IPS?
IDS (Intrusion Detection System) monitors and alerts on suspicious activity, while IPS (Intrusion Prevention System) actively blocks and prevents threats in real-time.
What is Firewall IDS and IPS?
Firewall IDS and IPS are security mechanisms integrated into firewalls to detect (IDS) and prevent (IPS) unauthorized access and attacks, enhancing overall network protection.
What is IDS in Networking?
IDS in networking is a system that monitors network traffic for suspicious activities or policy violations and generates alerts when potential threats are detected.
Why Do You Need Both IDS and IPS?
You need both IDS and IPS to ensure comprehensive security; IDS identifies and alerts on potential threats, while IPS actively prevents and mitigates those threats, providing layered protection.