Written By:
Scott McAuley
Scott is the IT Director of Texas Management Group, and has been in the IT industry for 25 years.
In today’s data-driven world, the importance of database integrity cannot be overstated. Imagine the chaos of losing critical data due to unforeseen circumstances. This is where mastering Database Backup and Recovery becomes essential, ensuring that your valuable data is always safe, accessible, and intact.
Database Backup and Recovery is not just a technical necessity; it’s a strategic pillar for any organization. The ability to effectively safeguard and restore data can mean the difference between business continuity and disaster.
This article delves into the ten essential components of Database Backup and Recovery. From identifying the types of backups to implementing recovery strategies, we’ll cover everything you need to know to protect your data assets.
Join us on this journey to enhance your knowledge and skills in Database Backup and Recovery. This comprehensive guide promises to equip you with the tools and understanding to handle any data recovery scenario with confidence.
Key Takeaways
- Essential processes ensuring data availability during system failures or disasters, involving creating copies (backup) and restoring databases (recovery) when needed.
- Safeguards against data loss, ensures business continuity, meets compliance, facilitates disaster recovery, and mitigates human errors, enhancing customer trust and saving costs.
- Protects critical data from loss and minimizes downtime, requiring a comprehensive strategy with clear backup policies and regular testing.
- Involves creating a backup strategy, monitoring performance, and validating backups, with various recovery methods like file-level, volume-level, and disaster recovery.
- Establish clear backup policies, regularly test processes, implement redundancy, automate tasks, monitor performance, update strategies, and document procedures for effective backup and recovery.
Table of Contents
What is Database Backup and Recovery?
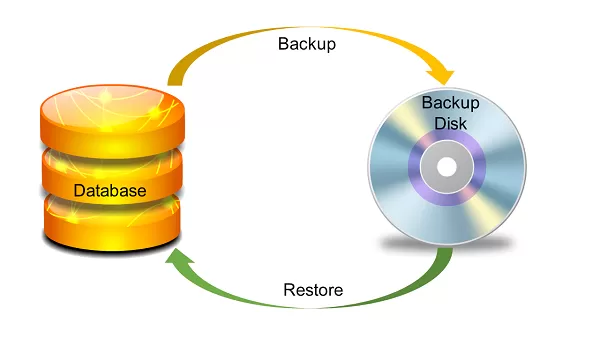
Database backup and recovery are essential processes that safeguard your data against loss and ensure its availability during system failures or disasters. These processes involve creating copies of your database (backup) and implementing strategies to restore the database to its original or a functional state (recovery) when needed.
Importance of Database Backup and Recovery

Protecting Against Data Loss
Data is a vital asset for businesses and organizations, and its loss can lead to significant financial losses and damage to reputation. Database backup and recovery techniques ensure that a copy of the data is always available for restoration in case of corruption, accidental deletion, or catastrophic failures. By regularly backing up databases, businesses can safeguard against data loss and quickly recover essential information, thus maintaining operational integrity.
Ensuring Business Continuity
In the event of a database becoming unavailable due to a failure or disaster, the resulting downtime can severely impact business operations. A robust backup and recovery plan minimizes this downtime by enabling rapid restoration of data, ensuring that businesses can continue their activities without prolonged interruptions. This continuity is crucial for maintaining customer trust and fulfilling service obligations.
Meeting Compliance Requirements
Many industries must adhere to stringent data protection and privacy regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX. Regular backups and well-defined recovery procedures help organizations comply with these regulations by ensuring that data can be restored in compliance with legal requirements. Failure to comply can result in hefty fines and legal penalties, making compliance an essential aspect of data management.
Facilitating Disaster Recovery
Natural disasters, cyberattacks, and other catastrophic events can strike without warning, potentially crippling an organization’s IT infrastructure. A comprehensive backup and recovery strategy is critical for disaster recovery planning, enabling businesses to quickly recover from such events and minimize the impact on their operations. This preparedness is vital for maintaining resilience in the face of unforeseen disruptions.
Mitigating Human Errors
Human errors, such as accidental deletion or incorrect data entry, are common causes of data loss. Backup and recovery plans provide a safety net by allowing businesses to restore data to a previous state, effectively reversing the impact of such errors. This capability is essential for maintaining data accuracy and reliability.
Enhancing Customer Trust and Confidence
Customers and stakeholders expect businesses to handle their data with utmost care. Demonstrating a commitment to data protection through robust backup and recovery measures enhances customer trust and confidence. This trust is a critical component of customer relationships and can be a significant differentiator in competitive markets.
Cost Savings and Risk Management
Investing in backup and recovery solutions can save businesses substantial amounts of money in the long run. The cost of implementing these solutions is often far less than the potential financial losses from data breaches, system failures, or prolonged downtime. Additionally, having a solid backup and recovery plan helps manage and mitigate risks associated with data loss, providing a more stable and predictable business environment.
Peace of Mind for Business Leaders
Knowing that there is a reliable backup and recovery plan in place provides peace of mind to business leaders. They can focus on strategic initiatives and growth opportunities without the constant worry of potential data loss. This assurance is invaluable for maintaining a proactive and forward-thinking business approach.
Objectives of Database Backup and Recovery
A robust database backup and recovery plan serves two primary objectives: protecting critical data from loss and minimizing downtime in the event of a system failure.
By implementing a comprehensive backup and recovery strategy, businesses can ensure the availability and integrity of their data, mitigate the impact of disruptions, and maintain uninterrupted operations.
- Data Protection: The first objective of database backup and recovery is to safeguard critical data against loss. With regular backups, businesses can create copies of their data, ensuring that even in the event of hardware failure, software corruption, or accidental deletion, valuable information can be recovered.
- Business Continuity: The second objective focuses on minimizing downtime and ensuring business continuity. A well-designed backup and recovery plan enables organizations to quickly restore data and resume normal operations, minimizing the impact on productivity, service delivery, and customer satisfaction.
10 Key Components of a Database Backup and Recovery Plan
In today’s data-driven world, ensuring the integrity and availability of critical data is paramount for businesses of all sizes. A comprehensive database backup and recovery plan is essential for safeguarding against data loss, system failures, and other unforeseen events.
Below are the ten key components that form the backbone of an effective backup and recovery strategy, providing a robust framework for protecting valuable data assets:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Backup Strategy | Defines what data to back up, how often, and where to store it, ensuring data protection and availability. |
| Data Retention Policies | Specifies how long backups are kept and when to delete them, balancing retention with storage cost. |
| Backup Storage | Chooses secure, scalable storage solutions (on-premises, cloud, or hybrid) for backup data. |
| Disaster Recovery Plan | Outlines steps for data recovery in case of major data loss, including RTOs and RPOs. |
| Backup Testing and Validation | Regularly tests and validates backups to ensure they can be successfully restored. |
| Security Measures | Implements encryption, access controls, and secure protocols to protect backup data. |
| Monitoring and Alerting | Monitors backup processes and alerts for any issues or failures to ensure timely interventions. |
| Documentation | Provides detailed instructions and configuration details for backup and recovery processes. |
| Regular Reviews and Updates | Continuously reviews and updates the plan to meet evolving business needs and technology advancements. |
| Staff Training and Preparedness | Trains staff on backup and recovery procedures to ensure they can handle data loss events effectively. |
1. Backup Strategy
A well-defined backup strategy is the foundation of any effective database backup and recovery plan. It involves determining what data needs to be backed up, how frequently backups should be performed, and where the backups will be stored. A robust backup strategy enables businesses to protect critical data and ensure its availability in the event of a system failure or data loss.
2. Data Retention Policies
Data retention policies outline how long backups will be stored and when they will be deleted. These policies are essential for managing disk space and ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently. By establishing clear data retention policies, businesses can strike a balance between retaining backups for an appropriate period and avoiding unnecessary storage costs.
3. Backup Storage
Choosing the right backup storage solution is crucial for preserving the integrity and accessibility of backup data. Whether it’s on-premises storage, cloud storage, or a combination of both, the backup storage should provide secure and scalable storage capacity. A reliable backup storage solution ensures that backups can be quickly accessed and restored when needed.
4. Disaster Recovery Plan
A disaster recovery plan is a comprehensive strategy that outlines the steps to be taken in the event of a major data loss or system failure. It includes provisions for backup and recovery operations, defines recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs), and identifies the roles and responsibilities of key personnel. A well-designed disaster recovery plan is essential for minimizing downtime and ensuring a swift recovery.
5. Backup Testing and Validation
Regularly testing and validating backups is crucial for ensuring their reliability and effectiveness. Backup testing involves simulating various disaster scenarios and verifying that backups can be successfully restored. By conducting regular backup testing, businesses can identify any issues or gaps in their backup processes and make necessary adjustments to enhance their data protection capabilities.
6. Security Measures
Implementing robust security measures is essential for safeguarding backup data from unauthorized access or tampering. These measures may include encryption, access controls, authentication mechanisms, and secure transmission protocols. By securing backup data, businesses can ensure the confidentiality and integrity of their critical information.
7. Monitoring and Alerting
Monitoring the backup process and receiving real-time alerts for any issues or failures is crucial for maintaining the effectiveness of a backup and recovery plan. By implementing monitoring and alerting mechanisms, businesses can proactively identify and address any issues that may impact the reliability or timeliness of backups. Monitoring also allows for quick intervention and resolution of any potential backup failures.
8. Documentation
Comprehensive documentation of backup and recovery procedures is essential for ensuring consistency and clarity in the execution of these processes. Documentation should include step-by-step instructions, configuration details, and any relevant troubleshooting information. Clear and accurate documentation enables both technical and non-technical personnel to understand and follow backup and recovery procedures effectively.
9. Regular Reviews and Updates
Ongoing reviews and updates of the backup and recovery plan are necessary to adapt to changing business needs, technology advancements, and emerging threats. Regular reviews help identify any shortcomings or areas for improvement in the backup and recovery processes. By continuously assessing and updating the plan, businesses can enhance their data protection capabilities and align them with evolving requirements.
10. Staff Training and Preparedness
Training staff members on backup and recovery tools and procedures are essential for ensuring their competence and preparedness in handling lost data or system failures. Adequate training enables personnel to understand their roles and responsibilities, follow best practices, and respond effectively to backup and recovery incidents. By investing in staff training, businesses can enhance their overall data protection readiness.
Process of Database Backup and Recovery
The process of database backup and recovery involves several critical stages that ensure data is effectively backed up and can be quickly restored in the event of data loss or system failure. By understanding and implementing these processes, businesses can minimize downtime and protect their valuable data assets.
Here’s the key steps in the process of database backup and recovery:
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Create a Backup Strategy | Define backup frequency, type (full, incremental, differential), schedule, and retention policies. |
| Backup Data | Use backup software to create copies of the database at regular intervals (external drives, NAS, cloud). |
| Monitor Backup Performance | Regularly check backups for success and monitor disk space usage. |
| Validate Backup Data | Periodically test backups to ensure data integrity and accuracy. |
| Determine RPO (Recovery Point Objectives) | Define the maximum acceptable data loss measured in time. |
| Define RTO (Recovery Time Objectives) | Establish the target time to restore the database after a failure. |
| Perform Data Recovery | Initiate recovery process, restore data from the latest backup, and apply incremental backups/logs. |
| Document Backup Procedures | Maintain detailed documentation of backup and recovery processes. |
| Regular Reviews and Updates | Continuously review and update the backup and recovery plan. |
| Staff Training and Preparedness | Train staff on backup and recovery tools and procedures. |
1. Create a Backup Strategy
Define the frequency and type of backups (full, incremental, differential, transaction log, etc.) to be performed. Establish a backup schedule and retention policies to ensure data availability and optimize storage use.
2. Backup Data
Utilize reliable backup software to create copies of the database at regular intervals. Backup destinations can include external drives, network-attached storage (NAS), and cloud storage. Implement the 3-2-1 backup rule: keep three copies of your data, store two backup copies on different storage media, and keep one copy offsite.
3. Monitor Backup Performance
Regularly check backup processes to ensure they are running smoothly. This includes verifying the success of backups and monitoring disk space usage to prevent storage issues.
4. Validate Backup Data
Periodically test backups to ensure data integrity and accuracy. Validate that backup files are complete and free from errors, and that they can be successfully restored.
5. Determine Recovery Point Objectives (RPO)
Define the maximum acceptable amount of data loss measured in time. This helps determine how often backups should be performed to meet recovery needs.
6. Define Recovery Time Objectives (RTO)
Establish the target time within which the database should be restored after a failure. Consider the time required for data restoration, system configuration, and application recovery.
7. Perform Data Recovery
In the event of data loss, initiate the recovery process according to the defined strategy. Restore data from the most recent backup and apply incremental backups or transaction logs to bring the database up to date.
8. Document Backup Procedures
Maintain detailed documentation of backup and recovery processes. Include step-by-step instructions, configuration settings, and contact information for support resources. This ensures consistency and accuracy in backup operations and assists in training staff.
9. Regular Reviews and Updates
Continuously review and update the backup and recovery plan to adapt to changing business needs and technological advancements. Regularly assess the plan to identify areas for improvement.
10. Staff Training and Preparedness
Train staff on backup and recovery tools and procedures. Ensure they understand their roles and responsibilities and are prepared to respond effectively to data loss events.
How to Create a Database Backup and Recovery Plan
Creating an effective database backup and recovery plan is crucial for ensuring the security and continuity of your business’s critical data. Follow these five essential steps to develop a comprehensive plan:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Assess Data Volume and Criticality | Evaluate the amount of data and prioritize critical information. |
| Define Backup and Recovery Objectives | Set clear objectives for recovery point and recovery time. |
| Choose Backup Methods and Storage Solutions | Select backup types and decide on storage options (on-premises, cloud, hybrid). |
| Implement Backup Testing and Validation | Regularly test and validate backups to ensure integrity and accuracy. |
| Document Procedures and Train Staff | Maintain detailed documentation and train staff on backup and recovery processes. |
1. Assess Data Volume and Criticality
Evaluate the Amount of Data and Prioritize
- Volume Assessment: Calculate the total data size to be backed up.
- Data Criticality: Identify and prioritize critical data that requires immediate recovery.
2. Define Backup and Recovery Objectives
Set Clear Objectives for Backup and Recovery
- Recovery Point Objectives (RPO): Determine the maximum acceptable data loss measured in time.
- Recovery Time Objectives (RTO): Define the target time to restore the database after a failure.
3. Choose Backup Methods and Storage Solutions
Select Backup Types and Storage Options
- Backup Methods: Choose from full, incremental, differential, and transaction log backups.
- Storage Solutions: Decide between on-premises, cloud, or hybrid storage based on your needs.
4. Implement Backup Testing and Validation
Regularly Test and Validate Backups
- Integrity Checks: Ensure backup files are complete and error-free.
- Restoration Tests: Periodically restore backups to verify data accuracy and recovery process efficiency.
5. Document Procedures and Train Staff
Maintain Documentation and Provide Training
- Documentation: Keep detailed records of backup and recovery processes, including configurations and contacts.
- Training: Ensure staff are trained on backup and recovery procedures to handle data loss events effectively.
5 Types of Data That Needs to be Recovered
When creating a database backup and recovery plan, it is essential to identify the types of data that need to be recovered in case of a system failure or data loss. Different categories of data have varying levels of criticality and recovery requirements.
In this section, we will discuss the five types of data that businesses must prioritize when implementing a backup and recovery plan. Understanding these data types will help organizations ensure the comprehensive restoration of their critical information.
| Data Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Critical Business Data | Data vital for day-to-day operations and decision-making |
| Application Data | Data generated and managed by specific applications |
| Configuration and System Settings | Settings, preferences, and configurations of IT systems |
| User Data | Data generated and stored by individual users |
| Compliance and Regulatory Data | Data required for legal and regulatory compliance |
1. Critical Business Data
Critical business data refers to the data that is vital for the day-to-day operations and decision-making of an organization. This may include financial records, customer information, sales data, inventory data, and other proprietary information. Recovering critical business data is crucial for maintaining business continuity and minimizing financial losses in the event of data loss or system failure.
2. Application Data
Application data includes the data generated and managed by specific software applications used by a business. This may include customer relationship management (CRM) data, enterprise resource planning (ERP) data, project management data, and other application-specific data. Recovering application data is essential for ensuring the seamless operation of business applications and maintaining productivity.
3. Configuration and System Settings
Configuration and system settings data encompass the settings, preferences, and configurations that define the behavior and functionality of an organization’s IT systems. This includes network configurations, server settings, security settings, user access controls, and other system-related information. Recovering configuration and system settings data is critical for restoring the organization’s IT infrastructure and maintaining the security and integrity of the systems.
4. User Data
User data refers to the data generated and stored by individual users within an organization’s systems and applications. This includes user-generated files, documents, emails, and other user-specific information. Recovering user data is essential for preserving individual productivity, collaboration, and ensuring that users have access to their personal files and information.
5. Compliance and Regulatory Data
Compliance and regulatory data encompass the data that organizations are legally obligated to retain for compliance purposes. This may include financial records, customer data privacy information, healthcare records, and other industry-specific regulatory data. Recovering compliance and regulatory data is crucial for meeting legal requirements, avoiding penalties, and maintaining the trust of customers and stakeholders.
Difference Between Backup and Recovery
While backup and recovery are closely related concepts, it is essential to understand the key differences between the two. Backup refers to the process of creating copies of data, while recovery involves restoring data from those backups.
Backup is a proactive measure that involves taking regular snapshots of your data and storing them securely. It serves as a precautionary measure against data loss or corruption. The backup process creates duplicate copies of your files, ensuring that you have a secondary source of data in case the original files are lost or damaged. These backup files can be stored on local storage devices, remote servers, or cloud platforms.
On the other hand, recovery is a reactive process that comes into play when data loss or corruption occurs. It involves restoring the backed-up data to its original state or to a previous point in time. The recovery process ensures that you can retrieve and use your data even if the original files become inaccessible or compromised.
5 Types of Data Recovery
1. File-Level Recovery:
– Involves recovering individual files or directories that have been accidentally deleted, corrupted, or lost. This method restores specific files without affecting the entire system or database.
2. Volume-Level Recovery:
– Focuses on recovering entire storage volumes, such as hard drives, partitions, or logical volumes. It restores data at the volume level, including all files and directories contained within the volume.
3. Point-in-Time Recovery (PITR):
– Allows users to restore data to a specific point in time, typically using backups taken at regular intervals. PITR is useful for recovering data to a consistent state before a data loss event occurred.
4. Database-Level Recovery:
– Specifically designed for recovering databases and their associated objects, such as tables, indexes, and schemas. It ensures the integrity of database transactions and maintains data consistency during the recovery process.
5. Disaster Recovery:
– Comprehensive recovery process aimed at restoring entire IT infrastructures and business operations after a catastrophic event, such as natural disasters, hardware failures, or cyberattacks. It involves recovering data, systems, applications, and services to resume normal business operations.
5 Types of Database Backup
1. Full Backup:
– A complete copy of all data in a database or system is created during a full backup. It captures all files, folders, and database contents, providing a comprehensive snapshot of the entire dataset. While full backups offer robust data protection, they require significant storage space and may take longer to complete.
2. Incremental Backup:
– Incremental backups only store changes made to the data since the last backup, reducing storage requirements and backup time. Each incremental backup captures changes made since the previous backup, allowing for more frequent backups and faster recovery times. However, incremental backups rely on the integrity of previous backups for complete data restoration.
3. Differential Backup:
– Differential backups capture changes made to data since the last full backup. Unlike incremental backups, which only store changes since the last backup (full or incremental), differential backups accumulate changes since the last full backup. While they require more storage space compared to incremental backups, they offer faster data restoration by combining the latest full backup with the most recent differential backup.
4. Synthetic Full Backup:
– Synthetic full backups combine the benefits of incremental and full backups by creating a full backup from incremental backup files. This process eliminates the need for frequent full backups while providing the same level of data protection. Synthetic full backups improve backup efficiency and reduce storage requirements by consolidating incremental changes into a single full backup file.
5. Mirrored Backup:
– Mirrored backups involve replicating data to multiple storage locations simultaneously. This redundancy ensures data availability and resilience against hardware failures, disasters, or data corruption. Mirrored backups are commonly used for critical systems and databases that require continuous uptime and fault tolerance.
7 Best Practices for Database Backup and Recovery
When it comes to database backup and recovery, following best practices is essential for ensuring the effectiveness and reliability of the process.
In this section, we will outline seven best practices that organizations should consider when implementing a backup and recovery plan. These practices will help businesses optimize their data protection strategies.
| Best Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Establish Clear Backup Policies | Define frequency, scope, and retention of backups to ensure consistent protection of critical data. |
| Regularly Test Backup and Recovery Processes | Simulate various scenarios to verify backup integrity and identify issues before actual data loss. |
| Implement Redundancy | Create multiple backup copies in different locations to protect against data loss from failures or disasters. |
| Automate Backup Tasks | Reduce human error and ensure timely, consistent backups through automation. |
| Monitor Backup Performance | Use monitoring tools for real-time alerts and metrics to address issues proactively. |
| Regularly Update Backup Strategies | Periodically review and improve strategies to keep up with technological and business changes. |
| Document Backup Procedures | Maintain detailed, step-by-step documentation for performing backups and recovery tasks. |
1. Establish Clear Backup Policies
Establishing clear backup policies is the foundation of a robust backup and recovery plan. Clearly define the frequency and scope of backups, including which data should be backed up and how long backups should be retained. This ensures that all critical data is consistently protected and can be easily restored when needed.
2. Regularly Test Backup and Recovery Processes
Regularly testing backup and recovery processes is crucial to ensure that backups are successful and can be accurately restored. This involves simulating various scenarios to verify the integrity and reliability of backups. Testing also allows for identifying and resolving any issues or weaknesses in the backup and recovery procedures before a real data loss event occurs.
3. Implement Redundancy
Implementing redundancy in your backup strategy adds an extra layer of protection against data loss. Redundancy can involve creating multiple backup copies stored in different locations or using different technologies. By having redundant backups, you minimize the risk of losing critical data due to hardware failures, disasters, or other unforeseen circumstances.
4. Automate Backup Tasks
Automating backup tasks helps ensure consistency and reliability in the backup process. With automated backups, you reduce the risk of human error and ensure that backups are performed in a timely and consistent manner. This also saves time and resources, allowing your IT team to focus on other important tasks.
5. Monitor Backup Performance
Monitoring backup performance is crucial to identify any issues or inefficiencies in the backup process. Implement monitoring tools that provide real-time alerts and performance metrics to help you proactively address any problems. By closely monitoring backup performance, you can quickly identify and resolve issues, ensuring the integrity and availability of your backup data.
6. Regularly Update Backup Strategies
Regularly updating your backup strategies is essential to keep pace with evolving technologies, data volumes, and business requirements. Review your backup strategy periodically to identify any gaps or areas for improvement. Stay informed about new backup technologies and practices to ensure that your backup strategy remains effective and aligned with best practices.
7. Document Backup Procedures
Documenting backup procedures is crucial for ensuring consistency and clarity in the backup and recovery process. Create detailed documentation that outlines the step-by-step procedures for performing backups, restoring data, and managing backup infrastructure. This documentation serves as a valuable resource for your IT team and ensures that backup procedures can be followed accurately and efficiently.
Conclusion
Mastering database backup and recovery is essential for safeguarding your business’s critical data and ensuring uninterrupted operations. This article covered the ten key components of an effective backup and recovery plan, emphasizing the importance of a well-defined strategy, regular testing, robust security measures, and continuous updates.
By understanding these components and implementing best practices, you can protect your data from loss, meet compliance requirements, and maintain customer trust. Regularly review and update your backup strategies to adapt to technological advancements and changing business needs.
Invest in comprehensive backup and recovery solutions to secure your data, minimize downtime, and ensure business continuity. For further insights and expert guidance, visit texmg.com and explore our range of cost-effective IT services designed to safeguard your valuable information.
Ready to enhance your data protection strategy? Explore more with us today and take proactive steps to secure your business’s future.
Want to Ensure Your Data is Always Safe?
Gain insights from our blogs on backup best practices, and discover how our Managed Disaster Recovery Services provide comprehensive protection against data loss.
Secure your peace of mind today!
FAQ
What is the Main Purpose of Backup and Recovery?
The main purpose of backup and recovery is to safeguard data against loss, corruption, or accidental deletion by creating copies of it and providing mechanisms to restore it to a usable state in case of data loss or disaster.
What is the Difference Between Backup and Data Recovery?
Backup involves creating copies of data for protection, while data recovery is the process of restoring lost or corrupted data from these backups to its original state or a usable form.
How Does Database Backup Work?
Database backup involves making copies of a database’s data and log files, typically using specialized backup software, and storing them in secondary storage such as tapes, disks, or cloud storage for safekeeping and easy retrieval in case of data loss.
Why is it Important to Backup Data?
It is important to backup data to protect against various threats such as hardware failures, software glitches, cyberattacks, accidental deletions, and natural disasters, ensuring business continuity, compliance with regulations, and safeguarding critical information.